Grafik
Plate IX
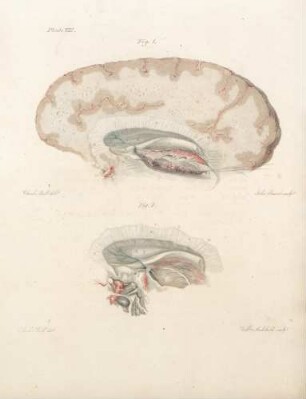
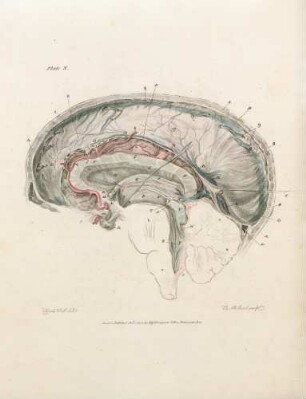
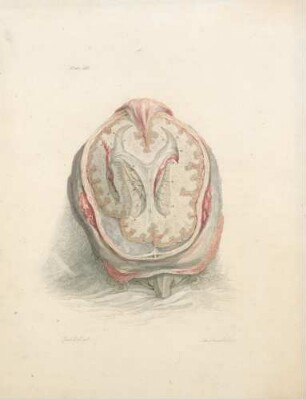
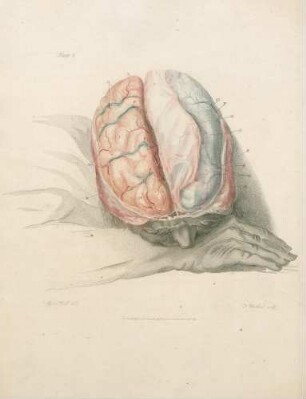
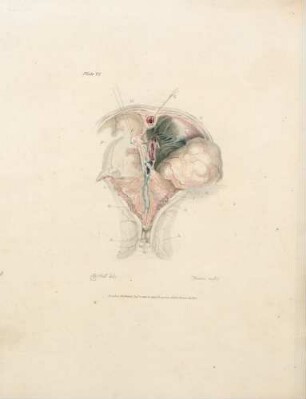
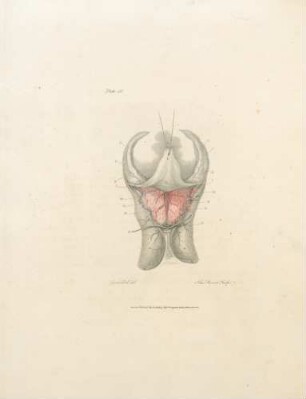
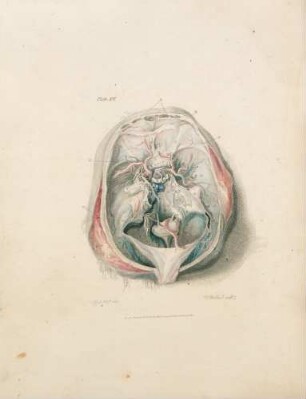
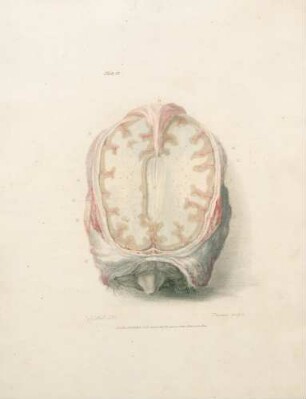
This, like the last Plate, is a partial view enlarged to the natural size, so as to enable us to represent the Nates and Testes, the Pineal Gland, the Iter ad quartum Ventriculum, the fourth Ventricle, the Valvula Vieussenii, and the Arbor Vitm, more minutely by a perpendicular section. a. The Sphenoid Bone, where it lies before the Pons Varolii. b. The Third Ventricle c. A Probe introduced into the Iter ad quartum Ventriculum, which we see passes down before the Nates and Testes, Posterior Comissure, and Pineal Gland. d. The Pineal Gland. e. The Pedunculi of the Pineal Gland, which stretch forwards in the Thalamus Opticus. f. The Comissura Cerebri Posterior, which we see to be formed by the medullary substance of the Nates, reflected so as to give, when we look from the cavity of the third Ventricle, the appearance of a medullary cord running across. We observe also the manner in which the Pineal Gland is attached to it. g. The Fornix. h. The Velum Interpositum, to which we see the Pineal Gland attached. i. The Vena Galeni, which carries the blood from those internal parts of the Brain to the fourth Sinus. k. The Nates. l. The Testes : or these k. l. are called the Tuberculi Quadrigemini, and we see that those surfaces are without the proper cavities of the Brain, and are involved in the delicate Pia Mater, which descends betwixt them and the Cerebellum. m. The Vascular Pia Mater, which insinuating betwixt the posterior lobes of the Cerebrum and the Cerebellum, passes down betwixt the Tuberculi Quadrigcmini, and also insinuating under the Fornix, is conveyed in form of the Velum Interpositum and Plexus Choroides, into the innermost recesses of the Brain; demonstrating to us, were it not self evident, that the external Pia Mater and the lining membrane of the Ventricles, are the same continued membrane. n. The Pons Varolii, or Tuber Annulare. We have also to observe the mixture of the cineritious matter seen in this section. o. The Section of the Medulla Oblongata, where the same strias are observed to be continued. p. The Cerebellum. q. The Arbor Vitae, or medullary part of the Cerebellum, ramifying through its substance. r. The Valvula Vieussenii. It is distinctly seen here to be a medullary Lamina, continued from the Testes obliquely backwards and downwards into the Crura Cerebelli, or termination of the Arbor Vitas, which forms thus the back and upper part of the fourth Ventricle. s. The Fourth Ventricle, which is now seen to be a cavity betwixt the Cerebellum, the Pons Varolii, and Crura Cerebelli, and which is seen to terminate upon the lower part by the adhesion of the Pia Mater. T. Medullary StrijE, which run up from the Calamus Scriptorius obliquely outwards. x. The Calamus Scriptorius, which is a sulcus formed by the posterior division of the Medulla Oblongata.
- Standort
-
Universitätsbibliothek Heidelberg
- Sammlung
-
UB Anatomische Illustrationen
- Inventarnummer
-
P 1242-4 Folio RES
- Sprache
-
Englisch
- Klassifikation
-
Stich (Gattung)
- Bezug (was)
-
Anatomie
Gehirn
Illustration
- Bezug (wer)
- Ereignis
-
Herstellung
- (wer)
- (wo)
-
London
- (wann)
-
um 1802
- Ereignis
-
Veröffentlichung
- (wer)
-
Longman
- (wann)
-
1802
- Ereignis
-
Veröffentlichung
- (wo)
-
London
- Letzte Aktualisierung
- 26.03.2025, 09:43 MEZ
Datenpartner
Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg. Universitätsbibliothek. Bei Fragen zum Objekt wenden Sie sich bitte an den Datenpartner.
Objekttyp
- Grafik
Beteiligte
Entstanden
- um 1802
- 1802