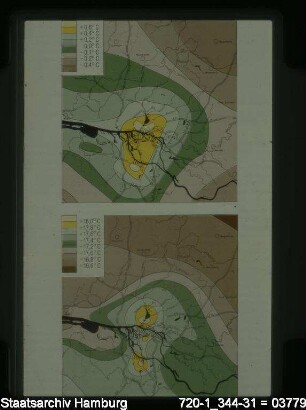
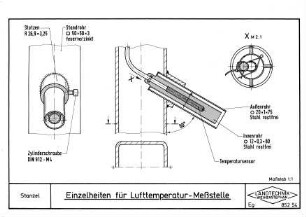
Geographische Gradienten der Lufttemperatur : Probleme ihrer Definition und Berechnung und ihre Anwendung
Abstract: Geographical gradients of air temperature are primarily required for the calculation of temperature values at arbitrarily chosen points away from weather stations. For more than a century the determination of the geographical vertical gradient of air temperature, the most important gradient in this, has essentially been arrived at by either of two methods: a) definition on the basis of the difference in temperature of two suitable weather stations at different altitudes (paired-stations method), or b) definition by balancing the differences in altitude and temperature of all weather stations in a given territory (regression method). The latter has been described repeatedly as the only consistent one, but it failed to prevail because its accuracy suffers greatly from the uniform treatment of weather stations in different topographical situations. The former allows consideration of influences of the position by selection of the stations, but fundamentally it lacks an unambiguous defi.... https://www.erdkunde.uni-bonn.de/article/view/1826
- Standort
-
Deutsche Nationalbibliothek Frankfurt am Main
- Umfang
-
Online-Ressource
- Sprache
-
Englisch
- Erschienen in
-
Geographische Gradienten der Lufttemperatur ; volume:31 ; number:4 ; year:1977
Erdkunde ; 31, Heft 4 (1977)
- Urheber
-
Hormann, Klaus
- DOI
-
10.3112/erdkunde.1977.04.01
- URN
-
urn:nbn:de:101:1-2410291105259.477283608298
- Rechteinformation
-
Open Access; Der Zugriff auf das Objekt ist unbeschränkt möglich.
- Letzte Aktualisierung
-
15.08.2025, 07:27 MESZ
Datenpartner
Deutsche Nationalbibliothek. Bei Fragen zum Objekt wenden Sie sich bitte an den Datenpartner.
Beteiligte
- Hormann, Klaus